Utility poles are a ubiquitous part of modern living. When everything is going right, people are so used to consistent power that they tend to ignore them completely. However, when there’s a power outage or another problem, countless calls to the power provider are made to get issues rectified as quickly as possible. In short, we are reliant on utility poles to function properly, or our daily lives tend to come to a standstill. They support the vital networks of electrical power, telecommunications, and cable services that we rely on daily.
However, despite their sturdy appearance, utility poles are subject to wear, tear, and environmental degradation over time. Regular inspections are essential to ensure their structural integrity and prevent potential hazards. In this article, we will delve into the significance of utility pole inspections, the reasons behind them, what inspectors must look for, the consequences of pole damage, and the detailed process of conducting thorough inspections.
To walk you through the entire utility pole inspection process in as much detail as possible, we’ll be using utility pole inspection workflow on the Cumulus Pro app. If you’re interested in trying it out for your next inspection job, you can take advantage of a 30 day free trial by downloading it from the App Store or Google Play.
Why is it Important to Inspect Utility Poles?
Utility pole inspections are paramount for several reasons:
- Safety: Ensuring the safety of both the public and utility workers is the primary concern. A damaged or weakened pole poses a significant risk of collapse, leading to potential injuries, property damage, and service interruptions.
- Reliability: Utility poles support critical infrastructure networks. Any failure or disruption in service can have far-reaching consequences, affecting businesses, emergency services, and everyday activities. Regular inspections help identify issues early, minimizing downtime and ensuring uninterrupted service.
- Compliance: Regulatory bodies often mandate routine inspections to maintain compliance with safety standards and regulations. Failing to adhere to these requirements can result in penalties and legal liabilities for utility companies.
What are Utility Poles Inspected For?
During inspections, utility poles are evaluated for various factors, including:
- Structural Integrity: Inspectors assess the overall condition of the pole, looking for signs of deterioration, damage, or structural weaknesses. Common issues include rot, cracks, insect infestations, and corrosion.
- Hardware and Attachments: Bolts, braces, crossarms, insulators, and other hardware components are inspected for proper installation, alignment, and integrity. Loose or damaged hardware can compromise the stability of the pole and its ability to support equipment.
- Ground Conditions: The area surrounding the pole is inspected for signs of soil erosion, water damage, or other factors that may undermine its stability. Adequate grounding is crucial to prevent electrical hazards and ensure proper functionality.
- Vegetation Management: Overgrown vegetation near utility poles can pose a fire risk and interfere with power lines. Inspectors identify and address vegetation that needs trimming or removal to maintain clearance and prevent hazards.
What Happens if a Utility Pole is Damaged?
The consequences of a damaged utility pole can be severe, impacting safety, reliability, and service continuity:
- Safety Hazards: A weakened or compromised pole is at risk of collapsing, posing dangers to people, vehicles, and nearby structures. Fallen poles can also cause electrical hazards and disrupt traffic flow.
- Service Disruptions: Damage to utility poles can lead to service outages for electricity, telecommunications, internet, and cable TV. Depending on the extent of the damage, restoring service may require significant time and resources.
- Financial Costs: Repairing or replacing damaged poles incurs financial expenses for utility companies. Additionally, liabilities arising from accidents or property damage can result in legal and insurance costs.
- Reputation Damage: Public perception of utility providers can suffer in the event of service disruptions or safety incidents. Maintaining a reputation for reliability and safety is essential for customer trust and satisfaction.
How to Conduct a Utility Pole Inspection
A comprehensive utility pole inspection involves several steps, utilizing various techniques and tools to assess the pole’s condition thoroughly. Now, let’s outline a step-by-step process for inspecting a utility pole using Cumulus Pro. If you’d like to follow along with a 30 day free trial, download it from the App Store or Google Play.
Below is an outline of the inspection process.
1. Preparation
- Gather necessary equipment, including safety gear (hard hat, gloves, safety glasses), inspection tools (probe, hammer, sounder, drill), and documentation materials (inspection forms, camera).
- Obtain necessary permits and permissions for accessing utility poles, especially if inspections involve excavation or bore testing.

2. Visual Inspection
- Begin by visually examining the pole from the ground level, looking for obvious signs of damage, such as cracks, splits, or leaning.
- Check for loose or missing hardware, rust stains, or signs of insect infestation.
- Inspect the area surrounding the pole for any signs of damage or hazards, such as erosion, flooding, or encroaching vegetation.
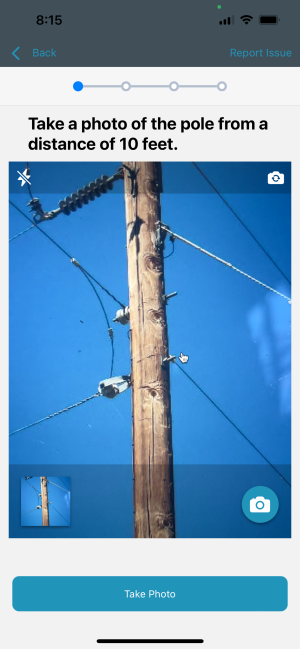
3. Probe Testing
- Use a probing tool to assess the pole’s structural integrity by gently probing areas suspected of decay or weakness.
- Insert the probe into cracks, crevices, or soft spots to determine the extent of deterioration.
- Pay attention to resistance and the depth of penetration, as these indicators can reveal the severity of internal damage.
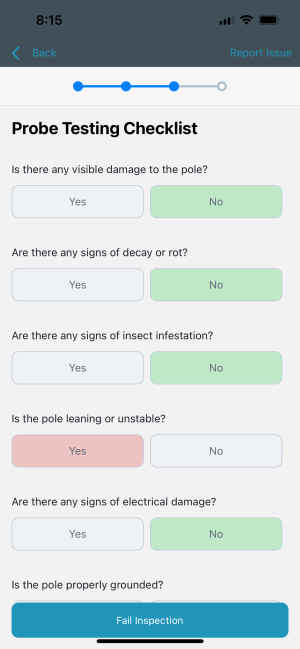
4. Sound Testing
- Tap the surface of the pole with a hammer or sounder to listen for changes in pitch or resonance.
- A hollow or dull sound may indicate internal decay or voids, whereas a solid, resonant sound suggests structural integrity.
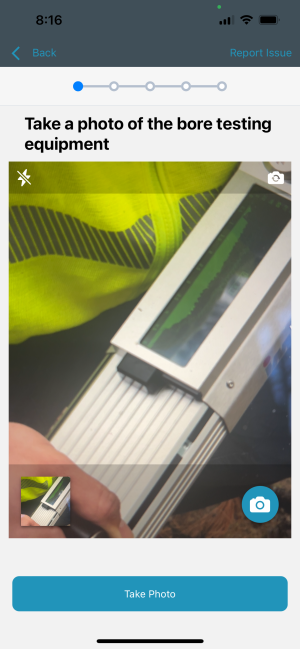
5. Bore Testing
- Drill small holes into the pole at strategic locations to collect core samples for further analysis.
- Examine the core samples for signs of decay, rot, or insect damage.
- Bore testing provides valuable insights into the pole’s condition without compromising its structural integrity.
6. Excavation (if necessary)
In cases where surface damage is suspected or additional assessment is required, excavation may be necessary.
Excavate the area around the pole base to inspect the foundation, underground hardware, and soil conditions.
Evaluate the integrity of grounding systems and address any issues that may compromise stability or conductivity.
7. Chip and Scrape Testing
Use a chisel or scraping tool to remove surface layers of wood, paint, or other materials for closer inspection.
Check for signs of decay, rot, or insect infestation beneath the surface.
Pay attention to the consistency and color of the wood, as well as the presence of moisture or fungal growth.
Conclusion
Utility pole inspections are a critical aspect of maintaining the safety, reliability, and functionality of essential infrastructure networks. By identifying and addressing potential issues proactively, utility companies can minimize risks, prevent service disruptions, and ensure the integrity of their systems.
Conducting thorough inspections using a combination of visual, tactile, and diagnostic techniques is essential for accurately assessing the condition of utility poles and prioritizing maintenance and repairs. Ultimately, prioritizing safety and reliability through regular inspections contributes to the well-being of communities and the efficiency of essential services.




